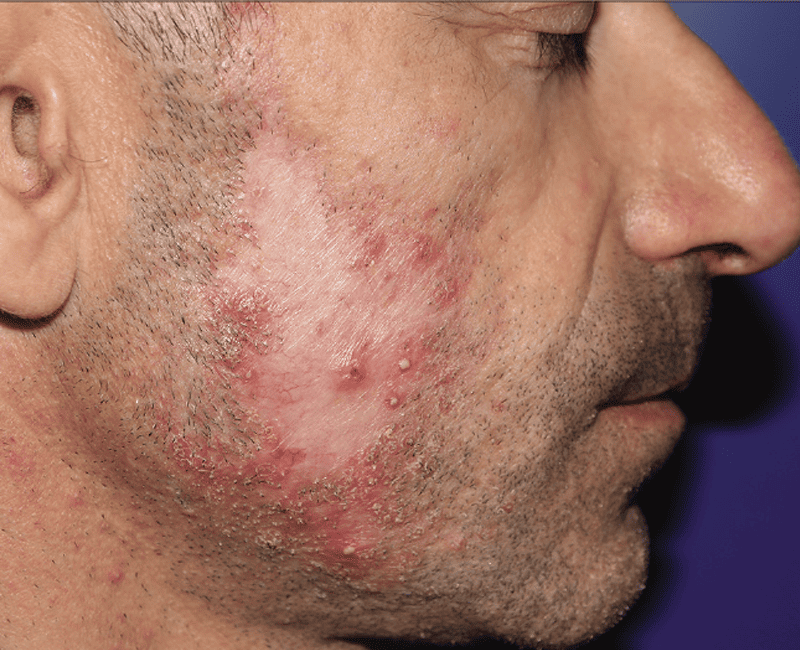
Beard infections can be a troublesome condition that affects the facial hair and the skin beneath it. Though many men grow beards for aesthetic and cultural reasons, improper beard hygiene can lead to various infections. These infections are often caused by bacteria, fungi, or other microorganisms that thrive in the warm, moist environment of the beard. Understanding the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options for beard infections is essential to maintaining healthy facial hair and skin.
Several types of infections can affect the beard area, including:
Beard infections can be triggered or worsened by various factors, including:
The symptoms of beard infections can vary depending on the type of infection, but they generally include:
To accurately diagnose a beard infection, a healthcare professional will examine the affected area and inquire about the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and shaving habits. In some cases, a sample of skin scrapings, hair, or pus may be taken for laboratory analysis to identify the specific microorganism causing the infection. Proper diagnosis is essential for selecting the appropriate treatment.
The treatment for beard infections depends on the type and severity of the infection:
Taking preventative measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing beard infections:
If you experience persistent or severe symptoms, such as pain, swelling, or fever, it’s important to see a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and promote faster recovery.
Beard infections can cause discomfort and affect the appearance of facial hair, but with proper hygiene, preventive measures, and timely treatment, they can be managed effectively. At FMS Skin and Hair Clinics we understand the type of infection and symptoms. And we ensure to address the condition promptly and provide effective treatment.
Address:
Door No. 8-2-293/82/A/725/A, Beside FMS INTERNATIONAL DENTAL CENTER Road No. 37, Hitech City Rd, near Daspalla Hotel, CBI Colony, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad, Telangana 500033
Email: [email protected]
Email: [email protected]
FMS Skin © 2020. All rights reserved. Terms of use and Privacy Policy