Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and while it is often associated with adolescence, it can persist well into adulthood.
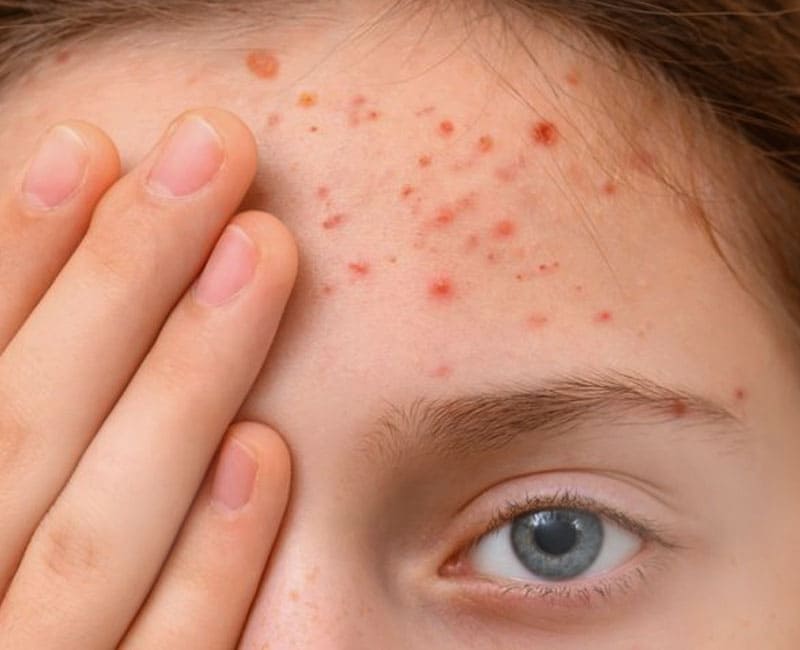
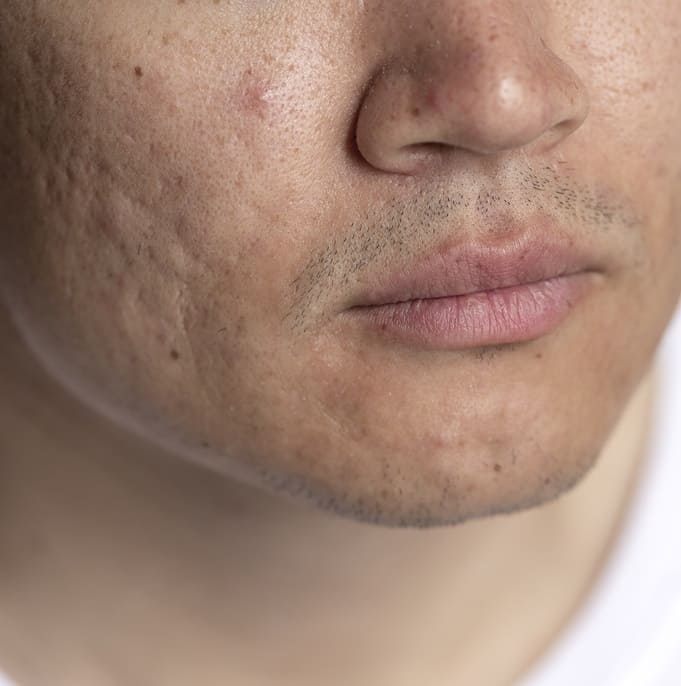
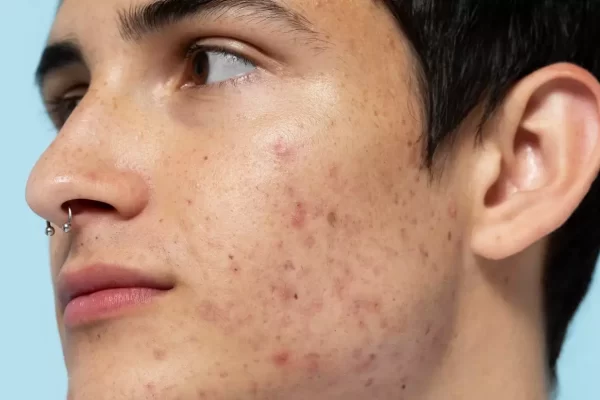
One area where acne tends to be particularly stubborn and noticeable is the forehead. Forehead acne can be frustrating and challenging to manage, but understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is the first step toward achieving clearer, healthier skin.
In this blog post, we delve into the intricacies of forehead acne, exploring its underlying causes, common symptoms, and effective treatment strategies. Whether you are dealing with occasional breakouts or chronic acne on your forehead, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to take control of your skin and achieve a smoother, blemish-free complexion.
Understanding Forehead Acne:
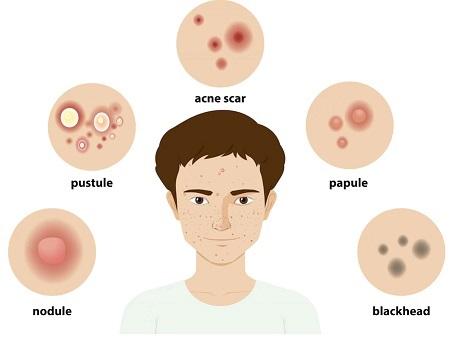
Forehead acne, also known as “Acne Vulgaris,” is characterized by the presence of inflamed or non-inflamed lesions on the forehead area. These lesions can range from small, red bumps (papules) and whiteheads (closed comedones) to pus-filled pimples (pustules) and larger, deeper cysts or nodules.
Underlying mechanism for Development of Forehead Acne:
Excess Sebum Production: The forehead, along with the rest of the face, contains sebaceous glands that produce an oily substance called sebum. When these glands become overactive, they can produce excess sebum, leading to clogged pores and acne breakouts.
Dead Skin Cells: The skin naturally sheds dead skin cells, which can accumulate on the surface and mix with sebum, forming a plug that blocks the hair follicles. This process, known as “comedogenesis,” can contribute to the formation of acne lesions.
What Causes Forehead Acne?
Oily Skin: The T-zone (the forehead, nose and chin areas) has more sebaceous glands, thus, more susceptible to pimples.
Genetics: Family history plays a significant role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to acne. If parents or siblings have a history of acne, the individual is prone to acne.
Inappropriate Skin Care and Makeup Products: Using skincare and makeup products that suit your skin type and needs is essential. Using comedogenic products can block skin pores, irritate skin & cause pimples.
Hair Care Products: Hair care products and certain hairstyles can contribute to forehead acne. Products like oils, pomades, and gels can clog pores if they come in to contact with forehead. Furthermore, hairstyles that cause friction or constantly touch the forehead can irritate skin and contribute to acne formation.
Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause or even patients on oral contraceptives can influence sebum production and contribute to acne flare-ups. Hormonal imbalances can also affect the skin’s natural pH balance, making it more prone to breakouts.
Over-Exfoliating: Cleansing is important, but it is also necessary not to overdo it. Cleansing too many times and over-exfoliating cause skin irritation. It can also strip your skin of its natural oils and barrier. Maintaining a balanced skincare routine with suitable products is important.
Digestive System Links: Face mapping associates the forehead with the digestive system, proposing that imbalances or issues in digestion may manifest as acne in this area. While scientific evidence for this connection is limited, focusing on balancing digestion through dietary choices and lifestyle habits is thought to potentially help in reducing forehead acne.
Poor Hygiene and Bacteria: Not cleansing your face regularly can lead to a build-up of dirt, oil and other deposits clogging your pores, causing acne. Touching your pimples or popping them can spread bacteria and aggravate acne. Further, dandruff and an oily scalp can also lead to forehead pimples.
Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) is a type of bacteria that resides on the skin’s surface. When hair follicles become clogged with excess sebum and dead skin cells, P. acnes can multiply rapidly, leading to inflammation and the formation of acne lesions.
Stress and Sleep Patterns
The occurrence of acne on the forehead can also be linked to stress and sleep patterns. Stress can trigger hormonal changes and inflammation, leading to acne. Additionally, inadequate sleep can impact the body’s ability to heal and regulate hormones, potentially exacerbating acne issues.
Symptoms of Forehead Acne:
Forehead acne typically presents with a variety of symptoms, which may vary in severity from person to person. Common symptoms of forehead acne include:
- Small red bumps or pimples on the forehead
- Whiteheads or blackheads (comedones)
- Painful, inflamed lesions (papules or pustules)
- Deep, cystic nodules beneath the skin’s surface
- Itching, irritation, or tenderness in the affected area
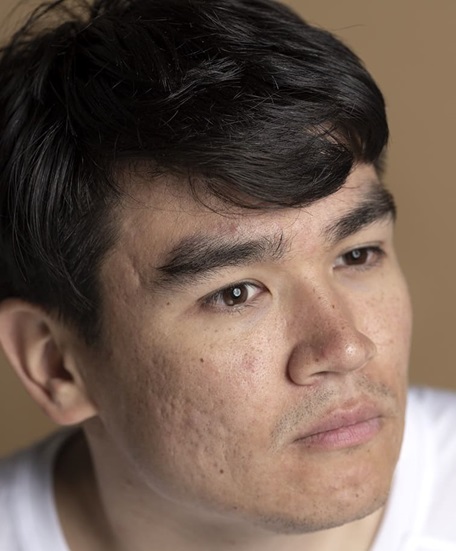
- Scarring or hyperpigmentation following severe breakouts
In addition to these physical symptoms, forehead acne can also take a toll on a person’s self-esteem and confidence, leading to feelings of embarrassment, frustration, or self-consciousness.
Treatment Options for Forehead Acne:
Fortunately, several effective acne treatments are available for managing forehead acne and achieving clearer, healthier skin. The choice of treatment will depend on the severity of your acne, your skin type, and any underlying factors contributing to your breakouts. Here are some common treatment options for forehead acne:
Topical Treatments:
Over-the-counter (OTC) acne products containing ingredients such as Benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids can help reduce inflammation, unclog pores, and promote skin cell turnover. Topical antibiotics or combination therapies (e.g., benzoyl peroxide with clindamycin or adapalene), may be recommended for more severe or persistent acne.
Oral Medications:
Oral Antibiotics: Such as tetracycline, doxycycline, or minocycline, may be prescribed to help control bacterial growth and reduce inflammation associated with acne.
Oral Contraceptives (Birth Control Pills): Containing estrogen and progestin hormones may be recommended for women experiencing hormonal acne, particularly around the time of menstruation.
Anti-Androgens: Spironolactone, Cyproterone Acetate, and Flutamide are some anti-androgens that help reduce the appearance of acne and blemishes by blocking androgen hormone receptors in the body. Therefore, these slow down the process of production of excess oil by the sebaceous glands.
Isotretinoin (Accutane): Isotretinoin is a potent oral medication that is highly effective in treating severe or cystic acne that has not responded to other treatments. It works by reducing sebum production, preventing clogged pores, and decreasing inflammation within the skin. Isotretinoin is typically reserved for severe cases of acne due to its potential side effects and the need for close monitoring by a healthcare provider.
Professional Procedures:
Chemical peels: This advanced treatment effectively treats mild to moderate acne. These plant-based extracts exfoliate your skin to get rid of the dirt, dead cells and excess sebum build-up in your pores, hence can help improve skin texture, reduce hyperpigmentation, and promote collagen production, leading to smoother, clearer skin.
Laser Light Based Therapy: Laser acne treatments are a sophisticated approach to managing acne, including forehead acne. One notable technique is the pulsed dye laser, which targets and reduces the inflammation associated with acne. This type of acne treatment is generally well-tolerated and can be effective in reducing both active acne and acne scars.
Other Light Treatments: Photodynamic therapy and blue light treatments are another category of light-based treatments for acne. These methods involve using specific light wavelengths to target acne-causing bacteria and reduce inflammation. Blue light therapy is particularly known for its antibacterial effects that work against acne.
In-office treatments such as corticosteroid injections or drainage of cystic lesions may be recommended for large, painful acne nodules or cysts that are at risk of scarring.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Wash your face with a gentle cleanser twice a day, as it helps remove excess oil and keep your skin clean. Choose moisturiser and sunscreen that suits to your skin type.
- Avoid wearing headbands or hats.
- Keep your scalp clean and free of dandruff. We recommend you consult a dermatologist to get a shampoo, preferably containing ketoconazole and zinc pyrithione, effective in controlling dandruff.
- Consult Dermatologist to build a good skin care routine according to your skin needs.
- Make sure you remove your makeup before sleeping, as it can clog your pores and cause pimples.
- Avoiding harsh or abrasive skincare products, as well as excessive scrubbing or picking at the skin, can help prevent further irritation and inflammation.
- Taking Zinc supplements and making dietary modifications, such as reducing consumption of high-glycemic foods, dairy products, and processed foods.
- Change pillow covers and bedsheets to fresh ones at regular intervals, to prevent bacteria.
- Drink enough water, eat nutritious food and engage in moderate physical activity at least 4 times a week for overall improvement in your health.
Forehead acne can be a persistent and frustrating skin condition, but with the right approach to treatment and skincare, it is possible to achieve clearer, healthier skin. By understanding the underlying causes of forehead acne, recognizing its symptoms, and exploring the various treatment options. Whether you opt for topical treatments, oral medications, professional procedures, or a combination of approaches, it is essential to work closely with a qualified & Expert Skin specialist to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your individual needs.
Consult FMS Skin & Hair Clinics, Best Cosmetic Skin Clinic in Hyderabad for
Advanced Cosmetic Skin Care Treatments
For Appointment Booking. Please call us or WhatsApp at 8885060760 Or Email Us at [email protected]

Author: Dr.Deepa